Islamist militant staff al-Shabab is fighting the UN-backed executive in Somalia, and has performed a string of assaults in neighbouring Kenya. the group, that is allied to al-Qaeda, has been pushed out of most of the primary cities it once controlled, nevertheless it continues to be a potent danger.
who’re al-Shabab?
Al-Shabab manner The Adolescence in Arabic.
It emerged as the radical early life wing of Somalia’s now-defunct Union of Islamic Courts, which controlled Mogadishu in 2006, earlier than being compelled out via Ethiopian forces.
There are numerous reviews of overseas jihadists going to Somalia to help al-Shabab, from neighbouring nations, besides because the US and Europe.
It is banned as a terrorist staff by means of both the u.s. and the united kingdom and is thought to have between 7,000 and 9,000 combatants.
 Symbol copyright AP Image caption Al-Shabab is suspected of hyperlinks to grenade assaults throughout Kenya
Symbol copyright AP Image caption Al-Shabab is suspected of hyperlinks to grenade assaults throughout Kenya
In The Past the worst attack was once on Nairobi’s Westgate shopping centre in 2013, whilst no less than SIXTY EIGHT other folks died.
In Westgate and different assaults, the militants spared Muslims, even as killing the ones unable to recite verses from the Koran.
There also are common gun and grenade attacks attributed to al-Shabab each in border spaces, the place many Kenyans are ethnic Somalis, and in Nairobi.
Al-Shabab says it is targeting Kenya as it has despatched its troops into Somali territory, the place they have joined the 22,000-sturdy African Union (AU) pressure combating the militants.
It performed an enormous attack on a Kenyan base in Somalia’s el-Ade town in January 2016, killing, in step with Somalia’s President Hassan Sheikh Mohamud, about 180 soldiers. The Kenyan army disputed the number, but refused to offer a death toll.
If the Somali president’s determine is accurate, it might be the deadliest ever attack by way of al-Shabab.
Media captionFrom Kenya, Alastair Leithead explores aftermath of the el-Ade battle
Al-Shabab has additionally set up a recruiting network in Kenya, together with across the port city of Mombasa, which has a big Muslim population.
Al-Shabab money objectives dissatisfied Kenyans
The cleric who expected he would be killed
How much of Somalia does al-Shabab keep watch over?
although it has misplaced keep an eye on of most cities and towns, it nonetheless dominates in lots of rural spaces.
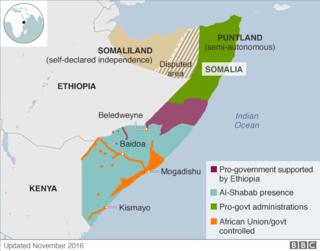
It used to be pressured out of the capital, Mogadishu, in August 2011 following an AU-led offensive, and left the vital port of Kismayo in September 2012.
The lack of Kismayo has hit al-Shabab’s funds, as it used to make cash by taking a minimize of the city’s worthwhile charcoal trade.
The AU-led flooring offensive has been backed by US air strikes, which ended in the killing of the gang’s leader, Aden Hashi Ayro, in 2008 and his successor, Ahmed Abdi Godane.
Al-Shabab is currently led through Ahmad Umar, additionally referred to as Abu Ubaidah. The United States has issued a $6m praise for info resulting in his capture.
Even Supposing the military operations are weakening al-Shabab, the gang continues to be in a position to perform suicide assaults.
It has additionally regained control of several cities, following the withdrawal of some Ethiopian troops.
Ethiopia mentioned it had pulled them out because of the monetary value of maintaining them in Somalia, though analysts said the solders had been wanted in Ethiopia to quell the most important anti-govt protests noticed in additional than 20 years.
What are al-Shabab’s international hyperlinks?
In a joint video launched in February 2012, former al-Shabab leader Ahmed Abdi Godane stated he “pledged obedience” to al-Qaeda head Ayman al-Zawahiri.
The teams have lengthy labored together and foreigners are identified to struggle alongside Somali militants.
There have also been a lot of stories that al-Shabab can have formed a few links with other militant groups in Africa, similar to Boko Haram in Nigeria and al-Qaeda within the Islamic Maghreb, based in the Sahara desert.
Al-Shabab debated whether or not to change allegiance to the Islamic State (IS) staff after it emerged in January 2014.
the gang ultimately rejected the idea, resulting in a small faction breaking away.
Africa’s militant Islamist teams
Jihadist groups across the world

what’s taking place in Somalia?
 Symbol copyright AFP Image caption Many Somalis have lived through drought, famine and warfare
Symbol copyright AFP Image caption Many Somalis have lived through drought, famine and warfare
Somalia has now not had an effective nationwide executive for more than twenty years, through which so much of the rustic has been a war-zone.
Al-Shabab won support by promising people safety. But its credibility was once knocked whilst it rejected Western meals help to fight a 2011 drought and famine.
With Mogadishu and different cities now beneath government keep an eye on, there is a brand new feeling of optimism and many Somalis have back from exile, bringing their money and skills with them.
Basic services and products corresponding to street lights, dry cleaning and garbage assortment have resumed in the capital.
But Somalia remains to be too dangerous and divided to hold democratic elections – the remaining one was once in 1969.
So, a complex system has been devised to choose a parliament and president, with extended family elders enjoying an influential function within the procedure.
Somalia’s rocky road to democracy
Lighting up Somalia
Connecting Mogadishu to the web
In pictures: Rebuilding Mogadishu






