 Image copyright NASA Symbol caption The glaciers in Vincennes Bay have proven the most important modification in behaviour in view that 2008
Image copyright NASA Symbol caption The glaciers in Vincennes Bay have proven the most important modification in behaviour in view that 2008
Dr Walker has been making the most of a new initiative at the company to process huge numbers of satellite photographs to get a extra resolved and more timely view of what is taking place in East Antarctica.
Previously, scientists have been conscious that the region’s Totten Glacier was once experiencing melting, almost definitely as a result of its terminus being affronted by means of warm water bobbing up from the deep ocean. just about the whole lot else in that part of the continent used to be thought to be stagnant, however.
The new satellite elevation and velocity maps modification this view. They make it transparent that local glaciers to Totten are also starting to reply in an identical way.
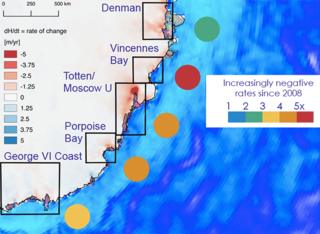
Marked change is detected within the Vincennes Bay and Denman spaces simply to the west, and in Porpoise Bay and at the George VI coast to the east.
Vincennes Bay – which contains the Underwood, Bond, Adams, and Vanderford glaciers – has probably the most pronounced loss in ice mass. Elevation is dropping at 5 times the speed it used to be in 2008 – with a total fall in height over the period of just about 3m.
“They Have Got additionally sped up about 3% from their 2008 speed, which sounds small however is important enough to modify the flux coming out of these glaciers as a result of they are very deep,” mentioned Dr Walker.
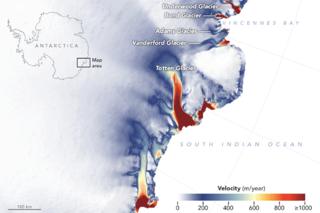 Image copyright NASA Image caption Totten has lengthy been recognised because the fastest moving glacier in East Antarctica
Image copyright NASA Image caption Totten has lengthy been recognised because the fastest moving glacier in East Antarctica
Once Again the melting culprit is probably going to be heat water that may be being pulled up from the deep by means of shifting sea-ice and wind styles within the region.
The changes which are occurring are still slightly delicate, and they’re simplest really discernible as a result of the brand new automated laptop gear so they can search during the millions of satellite tv for pc photographs taken of Antarctica.
Nasa is ready to widen get right of entry to to these tools through a venture called Inter-project Time Series of Land Ice Velocity and Elevation, or ITS_LIVE.
“I FEEL we can watch for that over the following five to 10 years, we’re going to have so much of observationally pushed discoveries, similar to what Catherine is making, on account of the brand new information that is coming on-line,” stated Alex Gardner, a glaciologist with Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California.
Jonathan.Amos-WEB@bbc.co.uk and practice me on Twitter: @BBCAmos






