 Symbol copyright Getty Photographs
Symbol copyright Getty Photographs
Chancellor Philip Hammond has used the Finances to ease the federal government spending squeeze as he declared that austerity was once “in the end coming to an end”.
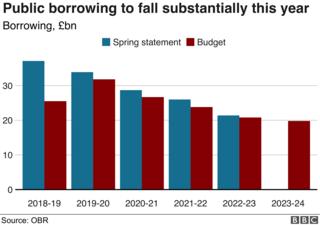
Against a backdrop of more potent tax receipts, Mr Hammond said borrowing this year can be £11.6bn less than projected in March, at £25.5bn.
Borrowing is anticipated to fall over the following five years.
Mr Hammond mentioned day-to-day spending budgets had been now expected to grow by means of round 1.2% a yr from 2019.
This is up from a typical contraction of 1.3% within the remaining Spending Evaluate in 2015.
Healthier public funds method the federal government can have used its borrowing windfall to get rid of the deficit in five years time.
It chose not to.
The OBR mentioned its downward revision to underlying borrowing over the next 5 years used to be the largest due to the fact that 2013.
On its personal, this would had been sufficient to succeed in the cheap surplus of £3.5bn in 2023-24, meeting the federal government’s goal of balancing the books by way of 2025.
By choosing to spend such a lot of the windfall as an alternative, the OBR defined this objective of balancing the books as “challenging from a wide range of views”.
It delivered that Mr Hammond confronted a stark selection: keep borrowing or reduce spending.
The OBR calculated that if the deficit saved falling on the comparable tempo past 2023-24 as in the coming 4 years, the federal government would be heading in the right direction to stability the books in 2028-29.
However, this will imply spending on government departments would need to beginning falling once more per head in actual terms.
Torsten Bell, director of the Solution Foundation suppose-tank, mentioned the federal government’s goal for the cheap surplus had effectively been “deserted”.
He tweeted: “Borrowing is admittedly being held at simply over £20bn endlessly.”
what’s the outlook for expansion?
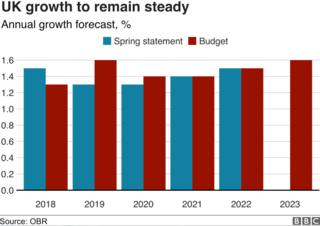
The executive’s impartial monetary watchdog left its forecasts for economic expansion widely unchanged.
The OBR mentioned the united kingdom financial system used to be expected to develop by 1.3% in 2018.
While that is fairly not up to the 1.5% expansion expected in March, financial enlargement is predicted to upward push to 1.6% in 2019, up from a prior projection of 1.3%.
Mr Hammond said wages have been these days growing at their fastest tempo in a decade.
Britain’s unemployment charge is now anticipated to fall to a contemporary 4-decade low of 3.7% subsequent year, with a robust jobs market anticipated to boost financial enlargement and tax revenues.
More Healthy public finances are expected to keep Britain’s debt share falling over the following 5 years, serving to the federal government to meet key fiscal laws.
 Budget 2018: At-a-look abstract What it approach for you Tech giants face virtual services tax Kamal Ahmed: Big spender Hammond Finances calculator
Budget 2018: At-a-look abstract What it approach for you Tech giants face virtual services tax Kamal Ahmed: Big spender Hammond Finances calculator 
How will Brexit impact the economic system?
Mr Hammond signalled that a good Brexit settlement would allow the Treasury to spend a “double deal dividend”.
He stated the economy might receive a lift from the top to uncertainty over Britain’s long run courting with the ecu, and a fair care for the ecu might additionally unencumber money set aside to give protection to the financial system in the experience of no deal.
Is it the top of austerity?
Samuel Tombs, chief UNITED KINGDOM economist at Pantheon Macroeconomics, mentioned govt coverage was once now expected to spice up economic enlargement subsequent year for the primary time considering the fact that 2014.
But Robert Chote, the chairman of the OBR, instructed that it was too early to mention austerity used to be over.
He mentioned the entire package of measures had a “acquainted Augustinian development of a near-time period giveaway followed via an extended-term takeaway”, expanding borrowing through £5.3bn in 2019-20 however decreasing it by £0.2bn via 2023-24.
Mr Hammond wants to deal with the scale of his Brexit struggle chest which he has put aside to give protection to the economic system from any shock within the experience of no deal.
Mr Tombs said: “The chancellor may have introduced higher spending for 2020-21 and beyond, but he is retaining some ammunition within the locker in case the financial system needs emergency improve.”
A 4-year freeze on working-age advantages can even continue.
John Hawksworth, chief economist at PwC, introduced that while total day-to-day spending is set to increase over the next five years, departments may need to wait till next yr to seek out out if any departments nonetheless faced spending cuts.
He said: “we can have to wait until the Spending Overview subsequent yr to make a final judgment as to whether austerity is really coming to an end.”






