 Symbol copyright EPA
Symbol copyright EPA
Local Weather talks in Poland have long gone into an extra day as negotiators try to agree the following steps forward for the Paris local weather agreement.
A Few delegates consider that poor coping with of the convention by the Polish executive is in the back of the delays.
Ministers from around ONE HUNDRED countries are collected in Katowice for the UN talks.
The majority of the details have been settled, however there is an ongoing stand-off over the query of carbon credit and carbon markets to scale back emissions.
Rich international locations frequently reduce their emissions through paying for carbon-cutting projects in other countries. However those programmes are very tough to police.
Fraud and double accounting have rendered lots of them nugatory – they’re incessantly dubbed hot air schemes.
Climate change talks run into extra time US, Saudis and Russia block climate report Failure to tackle warming ‘suicidal’
At those talks, Brazil has been pushing for a weaker set of regulations on carbon markets, in spite of strong opposition from many other international locations.
A steered compromise could see the discussions on markets kicked down the street to subsequent yr.
Ministers and negotiating teams say they’re satisfied to agree to this concept.
However they insist it’s up to the Polish presidency of the convention to guide the best way. and some negotiators are already unhappy approximately the way their Polish hosts have allowed the conference to meander.

Media captionNo more pork? 5 stuff you can do to help stop emerging world temperatures
On Friday, organisers released a new textual content intended to form the root of a deal. the description determination contains plans for a common rulebook for all international locations, with flexibility for poorer nations.
Developing countries are seeking for reputation and compensation for the impact of emerging temperatures.
The thought of being legally accountable for causing local weather amendment has lengthy been rejected through richer countries, who fear huge expenses well into the longer term.
Prof Myles Allen, from the School of Oxford informed BBC Information: “Climate amendment is already affecting many of us around the global and the people most influenced through local weather amendment are not those who have traditionally contributed so much to the issue.”
But many observers believed that, overall, some extent of progress has been made.
“It was never going to be great, no longer least for the reason that US is taking part in a laggard role, but i think we will be able to get a decent outcome, if it is framed in the proper method,” stated Alden Meyer from the Union of Involved Scientists.
In the final week, UN Secretary-Basic Antonio Guterres again to the assembly to attempt to push it to a successful conclusion.
“To waste this chance may compromise our ultimate absolute best likelihood to prevent runaway climate amendment,” Mr Guterres said. “It Would not just be immoral, it could be suicidal.”
And the previous president of the Maldives and now their lead negotiator, Mohamed Nasheed, mentioned that there can be “hell to pay” if nations did not come in combination on the summit to forestall temperatures shooting previous 1.5C.
Last weekend, scientists and delegates had been shocked while the us, Saudi Arabia, Russia and Kuwait objected to the assembly “welcoming” a up to date UN report on retaining global temperature rise to throughout the 1.5C limit.
The report mentioned the arena is now totally off course, heading extra in opposition to 3C this century.
Keeping to the most well liked purpose would wish “fast, a long way-attaining and unheard of changes in all aspects of society”.
Prof Allen stated: “For countries like Russia and Saudi Arabia, the place an enormous bite of their nationwide source of revenue arises from gross sales of fossil fuels, this is a much deeper drawback, and that’s the reason the place sticking issues are arising.”
What are the delegates trying to come to a decision?
Representatives from 196 states are trying to tackle a few very tricky questions about the rulebook of the Paris agreement, which comes into drive in 2020.
These are the rules in an effort to govern the nuts and bolts of ways international locations minimize carbon, provide finance to poorer international locations and ensure that everyone is doing what they are saying they are doing.
It sounds simple however is very technical. at the second international locations continuously have other definitions and timetables for their carbon chopping actions.
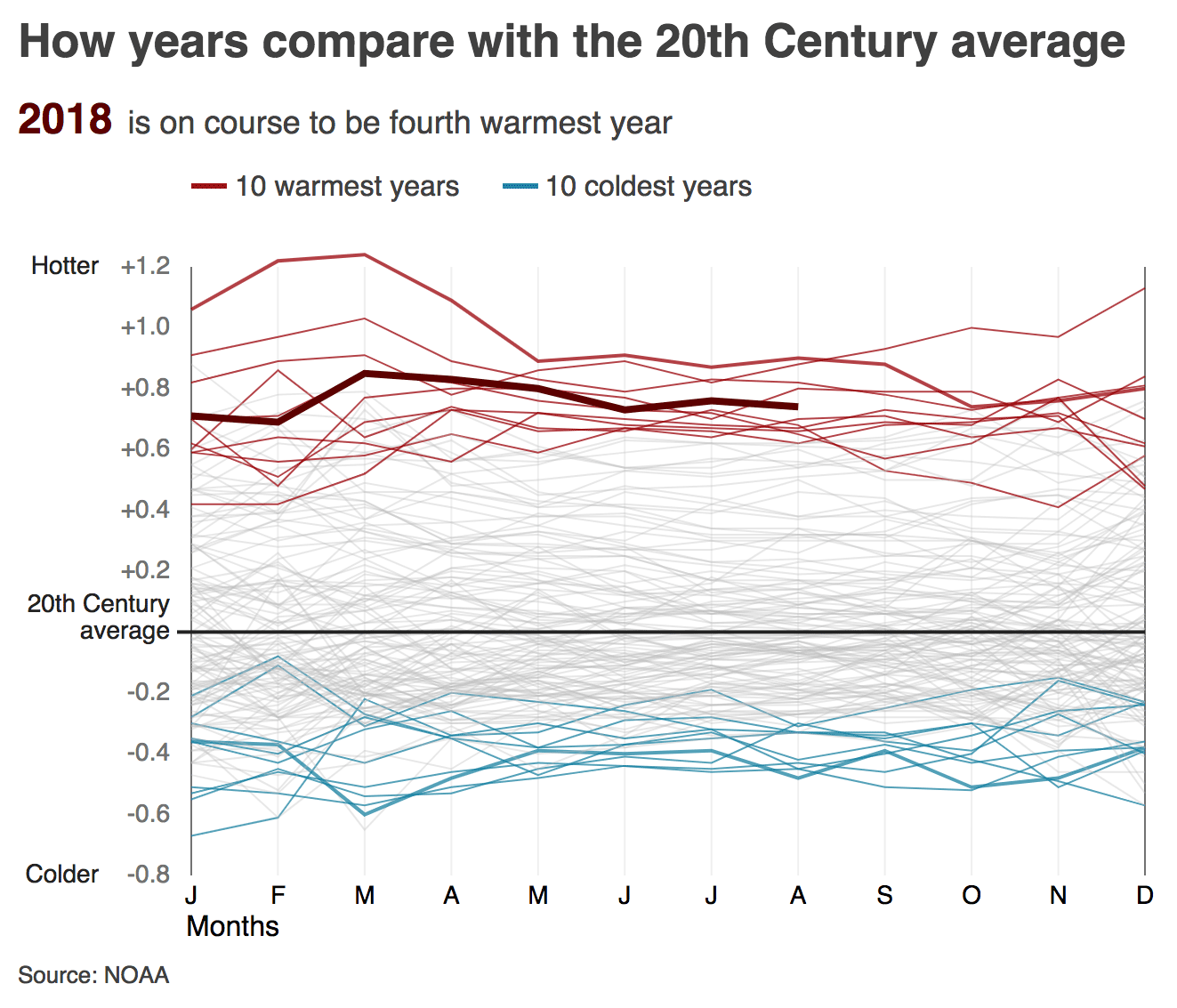
How years examine with the twentieth Century moderate
Poorer international locations need some “flexibility” in the regulations so that they are not beaten with regulations that they do not have the capacity to put into observe.
“Flexibility can mean so much of things and i believe a few countries are using that phrase to lengthen having to enforce laws, and others are involved as a result of they don’t have the capability to do it,” said Jennifer Morgan from Greenpeace.
As neatly because the rulebook, what else needs to be decided?
there’s a robust push to realize the science of the IPCC, which in advance this year produced a very important report on how the world would be impacted via temperatures emerging by means of 1.5C this century.
the verdict to welcome this report was rejected amid controversy in advance in the conference whilst Saudi Arabia, the us, Kuwait and Russia desired to simply be mindful of the record.
When consensus couldn’t be discovered, the text in regards to the IPCC was once dropped – to substantial wonder. that is being seen as something of a win for the ones four international locations.
“There are 196 countries within the UN and 192 counties agree,” stated Mohamed Nasheed.
“we’re just talking about 4 that don’t agree, and these 4 are taking us hostage.”
What about chopping carbon faster?
There has been a big push here for nations to up their ambition, to chop carbon deeper and with larger urgency.
Many delegates want to see a speedy increase in ambition sooner than 2020 to maintain the probabilities of staying below 1.5C alive.
Right now, the plans that international locations lodged as a part of the Paris settlement don’t get anyplace close to that, defined as “grossly insufficient” by one delegate from a local weather prone u . s ..

Business could also be searching for a signal from this assembly concerning the long run.
“Firms are ready to invest and banks are able to finance,” stated Carlos Salle from Spanish power conglomerate, Iberdrola.
“So we’d like that greater ambition in the policy to allow industry to move additional and faster.”
Who’s in point of fact responsible of those negotiations?
Poland holds the COP presidency but there has been concern that they lack an general picture of what must emerge from the meeting.
most of the people need to see a strong Paris “rulebook”, a commitment through nations to raise their objectives and carbon-reducing promises earlier than 2020 and a few clarity on how so much money might be delivered to poorer countries – as well as while it will arrive.
Even As some negotiators say the Poles are doing a good job in difficult cases, many are important, pronouncing they’re responding to the wishes of the wealthy not the terrible.
Follow Matt on Twitter.






