 Image copyright AFP Image caption Argentines are indignant that the government turned to the IMF (FMI in Spanish)
Image copyright AFP Image caption Argentines are indignant that the government turned to the IMF (FMI in Spanish)
Argentina is once again taking a look into the barrel of an economic main issue.
The foreign money is sliding, inflation rising and there may just well be a recession within the making.
The International Financial Fund (IMF) is providing an emergency mortgage.
it is all taking place underneath a government that was seen by way of the world financial markets as offering Argentina new desire, one which, underneath the management of President Mauricio Macri, held out the chance of balance and sustainable market-oriented financial policy that could begin to opposite a century of poor performance.
we look at six factors that have helped force the hindrance.
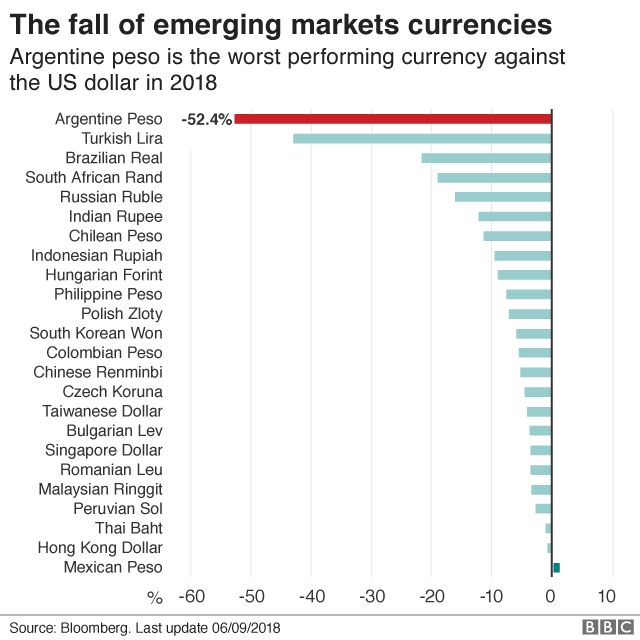
however the Peso has declined additional than some other.
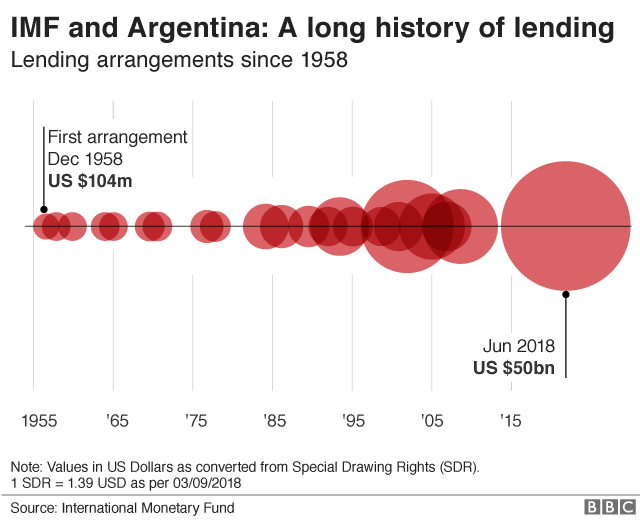
Argentina has IMF history
Once again, Argentina has grew to become to the IMF for monetary assist in a trouble.
It has agreed to lend Argentina a total of $50bn. Going to the IMF is a controversial move, especially so in Argentina.
IMF support usually comes with prerequisites that come with unpopular austerity. Many Argentines blamed the IMF for the former crisis in 2001. and there’s a historical past. Argentina had its first IMF programme sixty years ago.
Messy price range
The loss of confidence amongst world traders reflects issues approximately whether the federal government can meet all its debt payments and borrow the new money it must finance its spending.
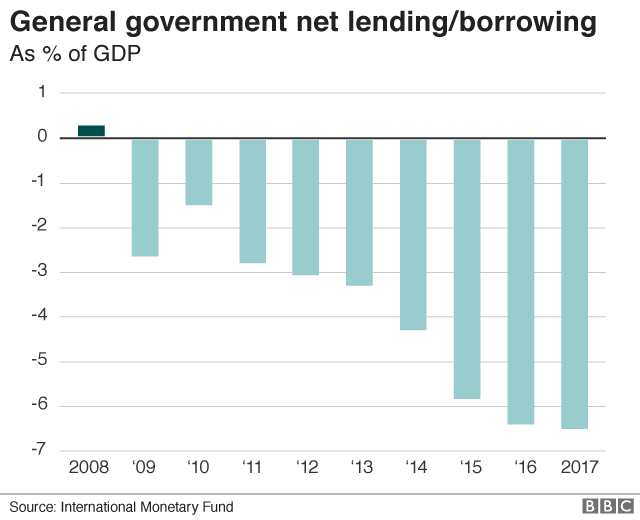
When President Macri took place of work at the end of 2015 the deficit in the government’s price range – how much more it spends than it takes in taxes – was huge. He desired to bring it down but adopted a gentle approach to financial reform.
There may be a rising deficit within the country’s global industry (or strictly speaking its current account). That has to be financed through foreign borrowing or investment, which is more and more challenging at a time while US interest rates are rising.
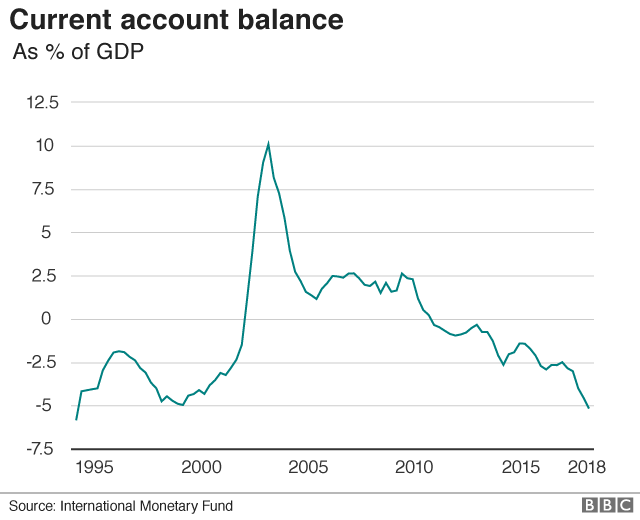
in reality the deficit were given fairly greater leaving Argentina at risk from anything that might make investors extra susceptible to drag their cash out.
Rocketing inflation
Argentina’s long standing inflation drawback is every other element within the challenge. the most recent determine is around 30%. THAT IS one in every of the highest in the international, even if not outstanding in Argentina’s historical past.
there has been a length of reasonably moderate inflation in the 2000s, however it didn’t final. (there is a gap in the graph, where the IMF concept the professional inflation figures unreliable).
The economic system (GDP within the graph) grew strongly within the years after the former drawback in 2001-2. But its contemporary efficiency has been extra asymmetric. Over the long run, Argentina’s efficiency has been dismal.
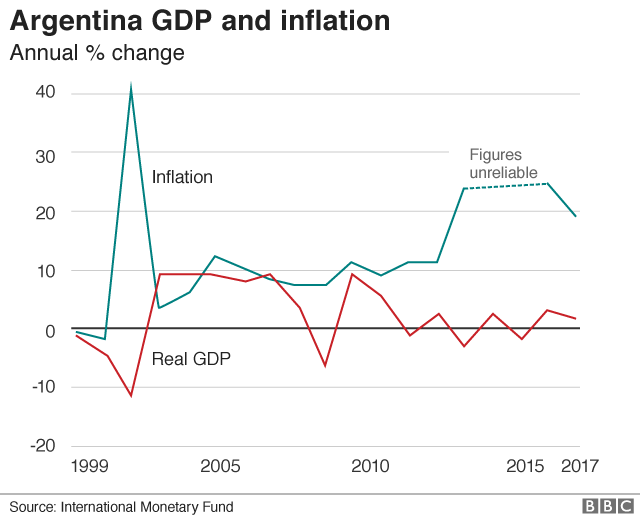
a hundred years ago, it was richer than many countries in Western Europe, in terms of monetary job (GDP) in line with person. Now it’s not up to half the degrees of France Germany and the united kingdom. The intervening century has been described as “one in all probably the most perplexing stories within the annals of contemporary financial historical past.”
interest rates soar
rates of interest have been greater sharply by the crucial bank in an effort to stabilise the Peso and convey inflation under regulate.
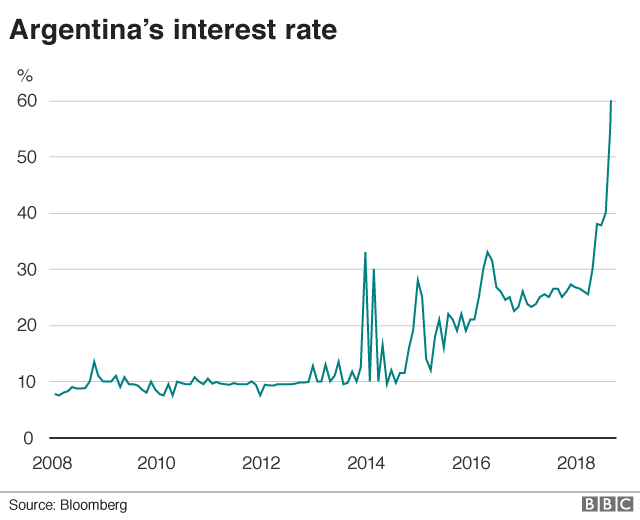
THAT MAY BE painfully high for customers and businesses that need or want to borrow.
even though the IMF bailout and the federal government’s reforms do paintings, it looks as if Argentina is, once more, in for a torrid time because it seeks to chart its approach via yet one more financial crisis.






