 Symbol copyright Getty Images Symbol caption The Value of Indonesia’s rupiah has been particularly laborious hit
Symbol copyright Getty Images Symbol caption The Value of Indonesia’s rupiah has been particularly laborious hit
Financial crises in Turkey and Argentina have resulted in talk of “contagion” – the danger of monetary problems in one country spilling over into others.
Turkey has struggled with a falling forex and irritating family members with the us.
A spiralling difficulty in Argentina prompted the government to announce austerity measures and to invite the World Monetary Fund (IMF) for an early liberate of a $50bn loan.
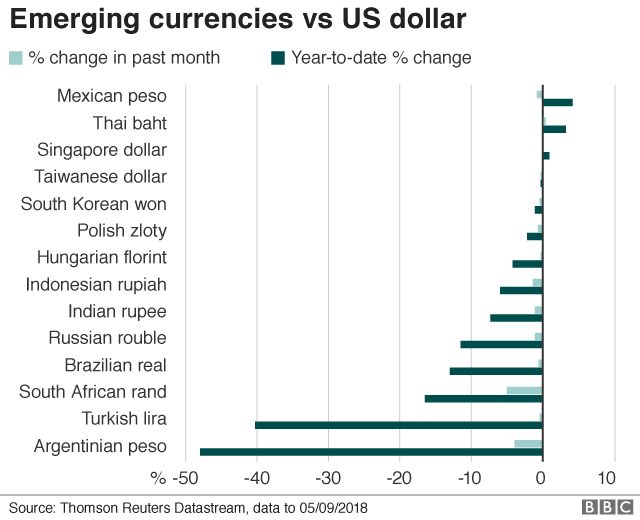
The sharp falls within the worth of Turkey’s lira and Argentina’s peso have led to fears that currencies from South Africa to Russia will apply suit.
In Asia, India’s rupee and Indonesia’s rupiah have already been hit.
 Symbol copyright Getty Photographs
Symbol copyright Getty Photographs
Alternatively, Joseph Gagnon at the Washington-based totally Peterson Institute for World Economics, says Asia has “very low industry links” with Argentina and Turkey, “so that isn’t so much of a worry”.
Rajiv Biswas, Asia Pacific chief economist for IHS Markit, also says business with Turkey is an not likely channel of contagion for Asia, for the reason that area is predicated extra heavily on massive economies reminiscent of China, Europe and the united states for their exports.
“The more vital concern for Apac Asia Pacific international locations would be if the Turkish economic problem leads to contagion to rising markets currencies and equities, which could doubtlessly trigger significant capital outflows from emerging markets,” he said.
Why are different emerging markets suffering?
The word “rising markets” refers to developing international locations in Africa, Latin America or Asia, at the same time as best economies equivalent to the u.s., the uk and Japan tend to have higher residing requirements and extra developed financial systems.
During an financial main issue, traders are inclined to sell riskier property, such as rising market currencies or shares, and hang directly to safer ones, similar to the u.s. greenback or govt bonds issued by means of best economies.
Julian Evans-Pritchard, a senior China economist at Capital Economics, says international locations that depend on cash from in another country and have overseas inflows of money into their stock and bond markets are in particular at risk of contagion.
“the chance is that once sentiment turns more poor, overseas traders start to pull out the ones finances, which has an affect on the exchange charge,” he said.
“For international locations that borrowed a lot in foreign currencies, on a regular basis in US bucks, this will make it tough for them to pay off their foreign exchange denominated debt. that is what took place in 1997 throughout the Asian financial challenge, for example.”
Why have India and Indonesia been hit?
In Asia, each India and Indonesia depend closely on foreign capital inflows, which is why their currencies have suffered in particular.
India, an oil uploading u . s ., has noticed its import invoice upward thrust at the side of higher oil costs and this has led to its current account deficit to widen, said Mr Biswas of IHS Markit.
A country that runs a present account deficit might depend on inflows of forex to finance spending and investments.
Indonesia, in the meantime, has low foreign currency echange reserves and a prime level of international possession in the local fairness and bond markets, Mr Biswas brought.
This makes it in particular susceptible to traders pulling their money out of the u . s ..
How about bank exposure?
differently contagion can spread is while banks in one u . s . a . personal assets in another u . s . that’s in hassle. the industrial issues can cause the price of these assets to fall.
When that occurs, buyers worry how a bank will take care of the falling worth of the property, and how this may occasionally have an effect on its ability to lend money to shoppers and other borrowers.
Such concerns weighed on Eu bank shares just lately, with investors worried about how much Turkish belongings they own.
The Financial Times stated that a wing of the eu Significant Bank was fascinated about the exposure of some of the eurozone’s biggest creditors to Turkey. The report stated Spain’s BBVA, Italy’s UniCredit and France’s BNP Paribas, all of that have important operations in Turkey, were particularly exposed.
 Symbol copyright Getty Pictures Image caption Turkey’s forex fall ended in fear over banks’ exposure to the financial system
Symbol copyright Getty Pictures Image caption Turkey’s forex fall ended in fear over banks’ exposure to the financial system
Spain’s banks are probably the most exposed to Turkey, in keeping with IHS Markit, bringing up knowledge from the Financial Institution for International Settlements.
They have approximately €81bn of publicity to Turkish belongings, and French banks have exposure to approximately €35bn.
But IHS Markit’s Mr Biswas said Asian banks’ exposure to Turkey was once restricted.
“within the massive image of the banking sectors of the Asian nations, this will now not be a serious negative think about their outlook,” he mentioned.






