 Symbol copyright Getty Photographs
Symbol copyright Getty Photographs
No Less Than EIGHTY people have been killed in wildfires in Greece, with blazes also pronounced as far aside as the US, Sweden, Canada and the united kingdom. it is a summer time that has seen an strangely high number of fires in a few nations.
An house comparable to twice the size of the united kingdom is burnt via wildfires in an ordinary year.
Most are in faraway areas such because the savannah grasslands of Africa and South America, or the boreal forests which stretch from western Alaska to japanese Siberia.
However we rarely listen about wildfires in such isolated places. It tends to be those which threaten lives, infrastructure, or herbal resources that hit the headlines.
Indeed, in Europe, the choice of fires up to now this yr is easily above reasonable – but no longer within the international locations which can be on a regular basis worst affected.
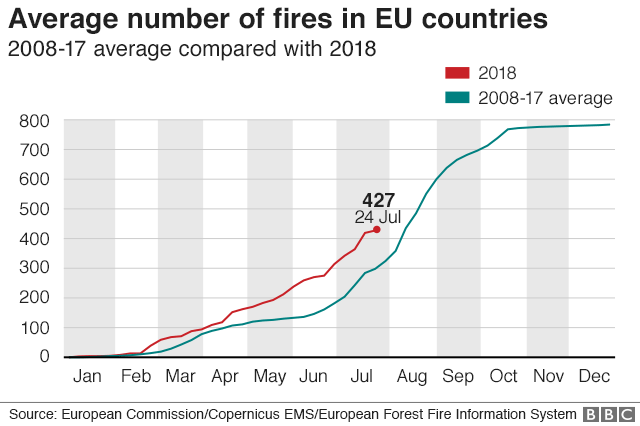
there were 427 blazes between 1 January and 24 July, when put next with a typical of 298 for the similar duration within the earlier decade.
However, very importantly, the realm they burned is purely about half what is on a regular basis noticed – 55,SEVEN-HUNDRED hectares, compared with 112,000 hectares.
In the u.s., the selection of fires this yr is slightly below average. Then Again, there has been a small increase within the space burned, from simply over 1.4m hectares to almost 1.6m hectares.
The most important amendment isn’t how many fires there have been, but where they are burning. The north-west of Europe is experiencing a rare heatwave.
This has introduced strangely dry stipulations that have allowed large fires in areas which typically see very few.
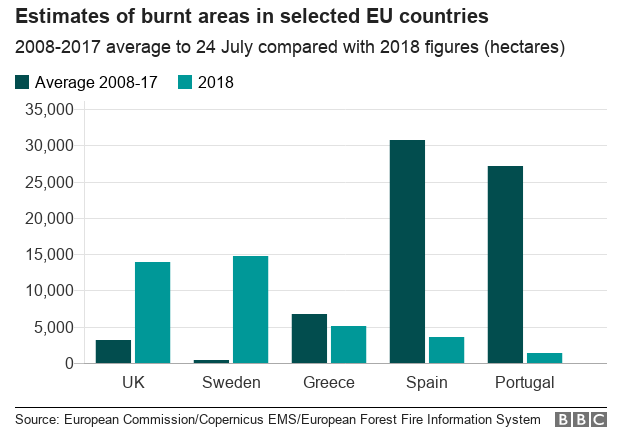
In the united kingdom the realm burned thus far – 13,888 hectares – is greater than four instances the common of the past decade. The fires have incorporated an area of peatland near Manchester and grassland in London.
In Sweden, the determine, 18,500 hectares, is an remarkable 41 instances the 10-year average. Dozens of fires have burned from the Arctic Circle all the way down to the Baltic Sea.
Other northern European nations including Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany and Latvia have noticed among 20 and 2 HUNDRED instances the traditional space burned.
In contrast, Mediterranean Europe – which typically sees a large choice of fires – has had a relatively cool and rainy spring and early summer.
In Italy and Croatia the area burned is definitely under average.
Spain and Portugal, which usually have fire injury over a greater area than some other Eu nations, have suffered slightly few fires – with best 12% and FIVE% of the average area burned, respectively.
On The Other Hand, hearth season is not over and there’s a danger that robust crops enlargement in portions of the Mediterranean may gas fires later in the coming months.
 Image copyright Getty Images Image caption A firefighter tackles wildfires in Lancashire
Image copyright Getty Images Image caption A firefighter tackles wildfires in Lancashire
Even As no unmarried issue explains sizzling weather around the global, professionals say climate amendment is bringing better and more widespread weather extremes.
It isn’t that the 2018 fires in the uk and Sweden will be the “new standard”, however they’ll be extra commonplace.
Upper temperatures around the world increase the danger of wildfires in many areas, but other elements are also vital.
To explain hearth, scientists and firefighters use something called the “fireplace triangle”: an ignition source, plus fuel reminiscent of dry plants and oxygen to maintain going.
Wildland firefighters additionally use the “30-30-30 rule” under which excessive hearth conditions are expected whilst temperatures are above 30C, relative humidity is under 30% and winds are greater than 30km according to hour (18.6 mph).
 Image copyright Getty Images Symbol caption Wildfires have blazed throughout Sweden this summer, with sizzling climate and persistent drought brought up because the primary causes
Image copyright Getty Images Symbol caption Wildfires have blazed throughout Sweden this summer, with sizzling climate and persistent drought brought up because the primary causes
Drought-troubled vegetation, such as the Swedish forests and the British moorlands, catches and incorporates fire extra simply than it might in a wetter year.
In different words, there may be more “fuel” available when the plants is dry.
Oxygen is instantly to be had within the air – in particular when wind fanatics the fires.
And resources of ignition are considerable the place there are folks, whether or not that may be a campfire, a spark from a power line, or arson.
In photos: Wildfire devastation ‘A friend died in the sea’ – Eyewitness bills How wildfires start and how to prevent them Reality Check: Mapping the global heatwave
Herbal ignition by means of lightning is common in some regions, such as the North The Us boreal forest, but in Europe the vast majority of fires are human-brought about.
The deadly fires in Greece are a primary example of climate being only one important issue.
Till a couple of days ago, Greece had experienced fewer fires than is conventional.
But, in a densely-populated region near Athens, the presence of villages and cities amid extremely-flammable pine forests and shrubland has had tragic results.
Building Up of “megafires”
 Symbol copyright Getty Photographs Symbol caption Spanish firefighters battle a wooded area fire in Portugal in 2017
Symbol copyright Getty Photographs Symbol caption Spanish firefighters battle a wooded area fire in Portugal in 2017
Unfortunately, such events have happened before.
Extra than ONE HUNDRED people were killed via wildfires in Portugal most effective closing yr and 173 people died within the Black Saturday Fires in Australia in 2009.
In recent a long time, there has been a rise of “megafires”.
Those are too big and fierce to be stopped, without reference to the efforts and instruments thrown at them.

More like this
how many folks do volcanoes kill? How a killer illness was stopped in its tracks Where a six-figure income is ‘low income’ Why ‘dangerous’ medication are still being used to regard ache 
While local weather amendment will have made extra gas to be had for such fires, human behaviour has also played a role.
In many rural areas of Europe land has been abandoned – resulting in the expansion of extra vegetation on the subject of and amongst houses. Other Folks steadily enjoy living or holidaying in woodland spaces, which also increases the danger of being in an instant suffering from fire.
Fortunately, it’s imaginable to cut back the risks this poses – by clearing “gas” with reference to homes and building fireplace shelters in spaces where the inhabitants may need them.
Educating people about the dangers and having evacuation plans in place can also reduce the threat to human lives and the economy.
We wish to adapt and be told the right way to coexist with fireplace.
Fire has been remodeling the Earth’s landscapes and plants for hundreds of thousands of years.
It is not going to move away.

About this piece
This research piece was once commissioned by way of the BBC from mavens running for an outdoor organisation.
Prof Stefan H. Doerr is a geography professor at Swansea School and editor-in-chief of the International Magazine of Wildland Fire.
Dr Cristina Santín is senior lecturer and analysis fellow within the biosciences department at Swansea School.

Edited by way of Duncan Walker






