 Image copyright Reuters
Image copyright Reuters
What began as a calm uprising towards Syria’s President Bashar al-Assad 5 years ago became a full-scale civil warfare that has left greater than THREE HUNDRED,000 folks dead, devastated the country and drawn in international powers.
Why is there a warfare in Syria?
Long earlier than the war began, many Syrians complained about high unemployment, common corruption, an absence of political freedom and state repression underneath President Bashar al-Assad, who succeeded his father, Hafez, in 2000.
In March 2011, pro-democracy demonstrations impressed by means of the Arab Spring erupted within the southern city of Deraa. The government’s use of fatal drive to overwhelm the dissent soon induced national protests hard the president’s resignation.
 Image copyright AP Image caption Protests in the southern city of Deraa in March 2011 had been suppressed by safety forces
Image copyright AP Image caption Protests in the southern city of Deraa in March 2011 had been suppressed by safety forces
because the unrest spread, the crackdown intensified. Opposition supporters started to take up fingers, first to defend themselves and later to expel security forces from their native spaces. Mr Assad vowed to overwhelm “foreign-subsidized terrorism” and restore state control.
 Symbol copyright Reuters Image caption The Town of Homs, dubbed “the capital of the revolution” suffered well-liked destruction
Symbol copyright Reuters Image caption The Town of Homs, dubbed “the capital of the revolution” suffered well-liked destruction
The violence swiftly escalated and the rustic descended into civil conflict as masses of rebellion brigades were formed to struggle govt forces for keep an eye on of the rustic.
 Image copyright AP Image caption Executive forces have lost keep an eye on of enormous swathes of the country to various armed teams
Image copyright AP Image caption Executive forces have lost keep an eye on of enormous swathes of the country to various armed teams
In essence, it has develop into greater than just a battle between the ones for or against Mr Assad.
A key issue has been the intervention of regional and world powers, together with Iran, Russia, Saudi Arabia and the United States Of America. Their military, monetary and political fortify for the federal government and opposition has contributed on to the intensification and continuation of the preventing, and grew to become Syria right into a proxy battleground.
Exterior powers have also been accused of fostering sectarianism in what used to be a widely secular state, pitching the country’s Sunni majority in opposition to the president’s Shia Alawite sect. Such divisions have inspired both sides to devote atrocities that have not only brought about loss of life but additionally torn aside communities, hardened positions and dimmed hopes for a political payment.
 Image copyright Reuters Image caption The northern Syrian town of Raqqa is the headquarters of the jihadist staff Islamic State (IS)
Image copyright Reuters Image caption The northern Syrian town of Raqqa is the headquarters of the jihadist staff Islamic State (IS)
Jihadist teams have additionally seized on the divisions, and their rise has introduced a further dimension to the struggle. Jabhat Fateh al-Sham, which used to be referred to as al-Nusra Front till it announced it was once breaking off formal ties with al-Qaeda in July 2016, is part of a powerful riot alliance that controls much of the north-western province of Idlib.
Meanwhile, so-known as Islamic State (IS), which controls huge swathes of northern and eastern Syria, is battling government forces, insurrection brigades and Kurdish teams, as well as going through air strikes through Russia and a US-led multinational coalition.
 Symbol copyright AFP Symbol caption Hundreds of Iranian-sponsored Shia militiamen are helping Syrian government forces
Symbol copyright AFP Symbol caption Hundreds of Iranian-sponsored Shia militiamen are helping Syrian government forces
Heaps of Shia militiamen from Iran, Lebanon, Iraq, Afghanistan and Yemen say they are fighting alongside the Syrian army to protect holy sites.
Why are such a lot of outside powers concerned?
 Image copyright Reuters Symbol caption Russia’s air campaign aimed to “stabilise” the government of President Bashar al-Assad
Image copyright Reuters Symbol caption Russia’s air campaign aimed to “stabilise” the government of President Bashar al-Assad
Russia, for whom President Assad’s survival is critical to keeping up its interests in Syria, introduced an air campaign in September 2015 with the aim of “stabilising” the federal government after a sequence of defeats. Moscow stressed out that it could aim most effective “terrorists”, but activists mentioned its moves basically hit Western-subsidized riot teams.
Six months later, having grew to become the tide of the warfare in his best friend’s favour, President Vladimir Putin ordered the “main part” of Russia’s forces to withdraw, saying their undertaking had “at the entire” been complete. Then Again, severe Russian air and missile strikes went directly to play a big function within the government’s siege of insurrection-held japanese Aleppo, which fell in December 2016.
 Symbol copyright Reuters Image caption Rebels have received handiest limited army the aid of Western powers
Symbol copyright Reuters Image caption Rebels have received handiest limited army the aid of Western powers
Shia power Iran is believed to be spending billions of dollars a year to reinforce the Alawite-dominated govt, providing army advisers and subsidised weapons, as well as strains of credit score and oil transfers. it’s also extensively said to have deployed hundreds of battle troops in Syria.
Mr Assad is Iran’s closest Arab best friend and Syria is the main transit aspect for Iranian weapons shipments to the Lebanese Shia Islamist motion Hezbollah, which has despatched thousands of opponents to beef up government forces.
 Image copyright Reuters Symbol caption A US-led coalition has been carrying out air moves on Islamic State militants in Syria considering the fact that 2014
Image copyright Reuters Symbol caption A US-led coalition has been carrying out air moves on Islamic State militants in Syria considering the fact that 2014
The U.s., which says President Assad is responsible for in style atrocities and will have to step down, has provided simplest restricted military help to “moderate” rebels, frightened that complex weapons might finally end up within the hands of jihadists. For The Reason That September 2014, the us has performed air moves on IS in Syria, but it surely has not deliberately attacked executive forces.
Sunni-ruled Saudi Arabia, that’s looking to counter the affect of its rival Iran, has been a big provider of army and fiscal help to the rebels, including people with Islamist ideologies.
 Symbol copyright Reuters Symbol caption Turkish troops are backing a Syrian rebellion offensive to take regulate of a northern border house
Symbol copyright Reuters Symbol caption Turkish troops are backing a Syrian rebellion offensive to take regulate of a northern border house
Turkey is another staunch supporter of the rebels, but it has additionally sought to contain US-subsidized Kurdish Widespread Coverage Gadgets (YPG) opponents who’re struggling with IS in northern Syria, accusing the YPG of being an extension of the banned Turkish Kurdistan Workers’ Birthday Celebration (PKK).
In August 2016, Turkish troops subsidized a revolt offensive to pressure IS militants out of one of the ultimate ultimate stretches of the Syrian aspect of the border now not managed via the Kurds.
What affect has the battle had?
 Image copyright Reuters Image caption There are no reliably accurate statistics at the choice of people killed or wounded in the fighting
Image copyright Reuters Image caption There are no reliably accurate statistics at the choice of people killed or wounded in the fighting
The UN says a minimum of 250,000 other people have been killed in the previous 5 years. Then Again, the organization stopped updating its figures in August 2015. The Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, a UNITED KINGDOM-primarily based monitoring staff, positioned the death toll at 310,000 in December 2016, even as a think-tank expected in February 2016 that the battle had led to 470,000 deaths, either directly or not directly.
more than 4.8 million other folks – most of them girls and children – have fled Syria. Neighbouring Lebanon, Jordan and Turkey have struggled to cope with one in every of the largest refugee exoduses in contemporary history.
 Image copyright Getty Pictures
Image copyright Getty Pictures
About 10% of Syrian refugees have sought protection in Europe, sowing political divisions as countries argue over sharing the load. a further 6.3 million people are internally displaced within Syria.
The UN estimates it is going to need $3.4bn (£2.7bn) to help the 13.5 million individuals who would require some type of humanitarian help within Syria in 2017. more than 7 million individuals are suffering from food lack of confidence and 1.75 million children are out of college.
 Image copyright AFP Image caption Virtually 1/2 Syria’s pre-battle population of 23 million has been displaced through the conflict
Image copyright AFP Image caption Virtually 1/2 Syria’s pre-battle population of 23 million has been displaced through the conflict
The warring parties have compounded the issues through refusing humanitarian companies access to many of the ones in want. Some 4.9 million people live in besieged or laborious-to-achieve spaces.
What’s being performed to finish the struggle?
 Image copyright Reuters Image caption Earlier makes an attempt by means of the UN to broker a political cost have failed
Image copyright Reuters Image caption Earlier makes an attempt by means of the UN to broker a political cost have failed
With neither side able to inflict a decisive defeat at the different, the world neighborhood way back concluded that just a political answer may just finish the conflict. The UN Security Council has called for the implementation of the 2012 Geneva Communique, which envisages a transitional governing frame with complete government powers “shaped at the foundation of mutual consent”.
Peace talks in early 2014, known as Geneva II, broke down after only two rounds, with the UN blaming the Syrian govt’s refusal to discuss opposition demands.
A yr later, the conflict with IS lent recent impetus to the search for a political solution in Syria. The U.s. and Russia persuaded representatives of the opponents to wait “proximity talks” in Geneva in January 2016 to discuss a security Council-counseled road map for peace, including a ceasefire and a transitional duration finishing with elections.
 Symbol copyright Reuters Symbol caption a local truce within the Homs suburb of al-Wair in December 2015 allowed rebels to be evacuated
Symbol copyright Reuters Symbol caption a local truce within the Homs suburb of al-Wair in December 2015 allowed rebels to be evacuated
the first spherical broke down even as nonetheless within the “preparatory” phase, as executive forces launched an offensive round Aleppo. The talks resumed in March 2016, after the united states and Russia brokered a nationwide “cessation of hostilities”. However they collapsed the next month as preventing intensified.
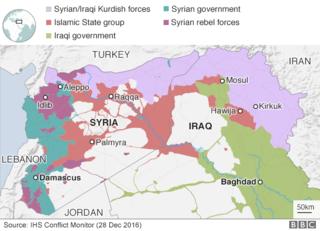
What is left of insurrection territory?
 Image copyright AFP Image caption A Number Of opposition-held districts and suburbs of Damascus are below siege
Image copyright AFP Image caption A Number Of opposition-held districts and suburbs of Damascus are below siege
the autumn of Aleppo method the federal government now controls Syria’s 4 biggest towns. But massive portions of the rustic are nonetheless held by other armed groups.
Rise Up opponents and allied jihadists are estimated to regulate about 15% of Syrian territory, according to the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights.
US officers mentioned in early December 2016 that there were 50,000 or more “moderate” rebels, focused in the north-western province of Idlib and the western Aleppo geographical region.
 Image copyright Reuters Symbol caption Al-Qaeda-associated jihadists are a key part of the rebel alliance controlling Idlib province
Image copyright Reuters Symbol caption Al-Qaeda-associated jihadists are a key part of the rebel alliance controlling Idlib province
Rebels also regulate smaller spaces within the valuable province of Homs, the southern provinces of Deraa and Quneitra, and the jap Ghouta agricultural belt out of doors Damascus.
Kurdish forces, who say they toughen neither the government nor the opposition, meanwhile control a lot of Syria’s border with Turkey, in addition as a large part of the rustic’s north-east.
And although they’ve suffered extensive losses within the earlier years, IS militants nonetheless hold massive parts of crucial and northern Syria, together with the town of Raqqa.






